~Siberia CTNP dominates winter 2020-21 in Northern Hemisphere
~New Refraction method helps identify the likeliest protogenesis system causing cold air buildups. Massive cooling areas can stem by very complex geophysical factors, luckily rendered simple by interface observations.
~ In one feedback loop, more snow comes from more clouds, in another loop the deep snow insulated ground cover saves the permafrost from rapidly rising reaching air in Arctic darkness, slowing the ground cooling process. In other words, darkness combined with lack of snow cover favors thermal radiation escaping to space, especially in areas far away from cyclones bringing warm air advection.
How does a winter area reach -57 C when it just was warmest year in history? CMC January 22 1800 UTC surface map. Note near sea ice shore its 20 to 25 C warmer,
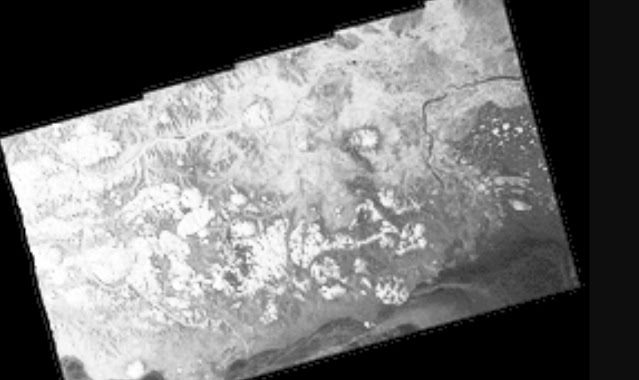
The closest readily available Polarview SAR image to CTNP cold center, suggests not so deep snow cover furtherest away from sea shore. The surface temperature CTNP is North of lake Baikal, a feature well above top of picture. Here we see and realize that heat from the Arctic Ocean is tempered mostly by first year sea ice, undeniably a great warming source many times greater than by greenhouse gases.
Extraordinary Refraction optical method directly immediately identifies when cold air is created, has confirmed 2021 winter far lesser capable in creating a very cold vortice on the Canadian side of the North Pole.
There are so many air freezing factors: differing snow layers, the shape of ice crystals and snow flakes, snow density, sea ice thickness, heat from covered sea water, cloud cover, sublimation rates, winds, precipitation columns.... These factors spaced over thousands of varying in nature square Kilometers, gives super computers a prediction deficit which most of us are familiar with. But optical refraction observations at Canadian side Arctic subsisting over thicker snow cover, has confirmed interface warmth being greatly favored, completely diminishing Northern Ellesmere and Greenland CTNP vortice to yield to Siberian freezing dominance.
Unfortunately, we lack specific snow density data, but
Canadian Cryosphere Watch snow cover thickness gives us some clues. Lake Baikal area, the current super cold spot (grey and red) has a deficit in snow as opposed to near the East Siberian sea. But look at Ellesmere
swamped with snow, in fact this Canadian Island, usually the home of the coldest Vortice of the Northern Hemisphere, currently has an excess of snow, a + 100 cm departure (purple). The surface temperatures there are 32 C warmer than Siberian Minimum. A more seasonal snow cover, less than 20 cm, has dense cement like snow, leaving hardly a footprint, making a person not sink in by a sublimation rendered thick upper crust . But a thicker snow layer stops the permafrost from teaming up with colder air from rapidly freezing the active ground layer, soil or rocks just below the surface. At present this thicker snow column is sheltering a significant sugar like layer just below top thinner sublimation induced hard crust. This granular snow, far less dense than top crust, prevented deep air cooling from appearing early during this long Arctic night.
Without mid winter deep snow, the Arctic becomes its perineal image, very cold, the engine of winter itself. Must keep in mind 2020 record low polar sea ice extent and thinnest as well, along with much longer wider areas of open sea water leading up to December, giving abnormal total precipitation columns. Southern Siberia, a vast area of land away from moisture sources, is a favorably dry place. However, as the end of long night approaches, the role of deeper snow will flip temperature effects. The permafrost active layer eventually will cool as much as earlier snow free grounds, causing its thick
snow carpet density to increase in later winter, guaranteeing a cold spring even during the gradual longer transitional sunny days, even well after the shinning midnight sun.
The dye is set, for now the CTNP will be Siberian until sun rays will rapidly warm its snowier free grounds, then so, Ellesmere will have a bitter cold spring under the coldest vortice in the world.
There are so many variables causing extremely cold vortices within the Polar Vortex, one can get lost in their causations. But it comes down to 2 features; the night, over suitable favorable surface freezing conditions. How deeply surface air cools depends on whether the interface between land/sea and atmosphere allows available surface heat to flee or to be caught in numerous feedback loops. WD January 22,2021