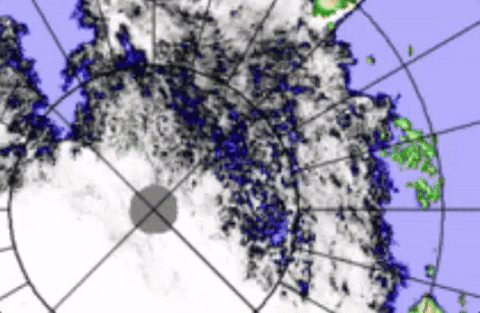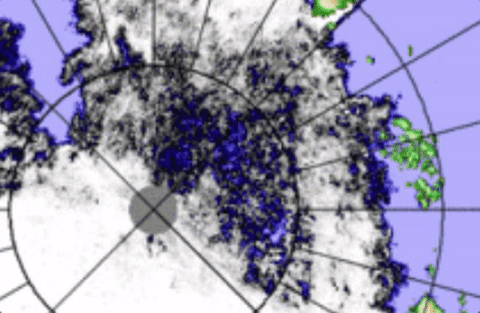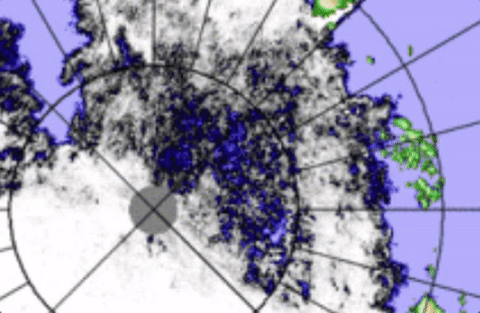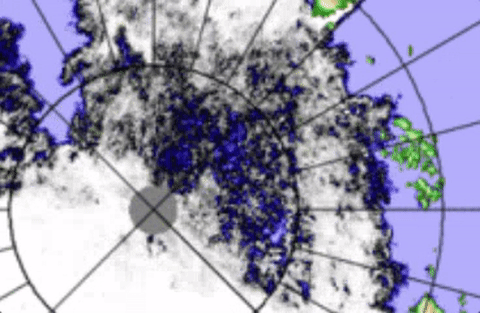
Apparent to all is the Transpolar Stream fill, in a mere day, affecting extent readings,
there is also false snow reflections particularly in the Canadian Arctic Archipelago, fallen floating snow appears as sea ice.
There was no real fill of the Transpolar Stream, just counterclockwise movement enabling by stress more shattering of larger ice pans, in other words greater scattering affecting the 15% sea ice grid numbers to rise. WDSep6,2016
Tuesday, September 6, 2016
Monday, September 5, 2016
Some effects of open water Transpolar Stream Current
It is not so obvious, there is the Atlantic front, where there is far less sea ice momentum pushing slowly to the North Atlantic:
August 26 to September 4 East of Spitsbergen. Appearing steady or moving North with a lot of melting.
 Fram Strait substantial extent gains with likely the most solid dense ice left unencumbered by TPS sea ice , hence the stretching out sea ice peninsula not with numerous Goodbye Waves, but heading certainly to melt at a much slower rate than Atlantic Front sea ice.WD Sept5,2016
Fram Strait substantial extent gains with likely the most solid dense ice left unencumbered by TPS sea ice , hence the stretching out sea ice peninsula not with numerous Goodbye Waves, but heading certainly to melt at a much slower rate than Atlantic Front sea ice.WD Sept5,2016
August 26 to September 4 East of Spitsbergen. Appearing steady or moving North with a lot of melting.
 Fram Strait substantial extent gains with likely the most solid dense ice left unencumbered by TPS sea ice , hence the stretching out sea ice peninsula not with numerous Goodbye Waves, but heading certainly to melt at a much slower rate than Atlantic Front sea ice.WD Sept5,2016
Fram Strait substantial extent gains with likely the most solid dense ice left unencumbered by TPS sea ice , hence the stretching out sea ice peninsula not with numerous Goodbye Waves, but heading certainly to melt at a much slower rate than Atlantic Front sea ice.WD Sept5,2016
Sunday, September 4, 2016
Transpolar Stream Current is now a free flowing sea river with broken sea ice all the way to the North Atlantic
~Another first in history
The collapse of what solid ice barrier remained at the shores of the Atlantic effectively has made the Transpolar Stream an open sea water river carrying sea ice directly to the Atlantic without the momentum of interconnected sea ice needed. This means a more rapid dumping of sea ice to melt.
A first in recorded history event, with ominous implications for the surviving sea ice.
2012 september 4 (above) had a substantial solid pack even with small leads on the Russian side of the North Pole, not at all like 2016 with a river of floating sea ice flowing all the way to the Atlantic. WD September 4,2016
The collapse of what solid ice barrier remained at the shores of the Atlantic effectively has made the Transpolar Stream an open sea water river carrying sea ice directly to the Atlantic without the momentum of interconnected sea ice needed. This means a more rapid dumping of sea ice to melt.
A first in recorded history event, with ominous implications for the surviving sea ice.
2012 september 4 (above) had a substantial solid pack even with small leads on the Russian side of the North Pole, not at all like 2016 with a river of floating sea ice flowing all the way to the Atlantic. WD September 4,2016
Wrangel bridge waves away: Goodbye!
Once sea ice melts to Goodbye Waves (slush), it doesn't take very long before these waves vanish to darkness. Here we have, very late in the season, prodigious melting not stopping, Goodbye waves are like the steam after water boils, prominent but fleeting, from common white to dying artistically, in 4 days a great deal of sea ice vanished, and the steam keeps burgeoning. WD September 4,2016
Wednesday, August 31, 2016
Atlantic Front retreating, likely because no substantial replenishment
~ And Goodbye Waves Palooza everywhere signifying great melting
Its a mess on the other side of the pack, with Goodbye Waves galore, the ex-Wrangel Ice bridge is rather a modern Art collection of rapidly disappearing sea ice. WD August 31,2016
Tuesday, August 30, 2016
Wrangel Island ice bridge no more, its a messy combination of very thin broken sea ice and Goodbye Waves
Goodbye Waves can give a problem with determining wether they are sea ice or as they really are slush:
 |
| Goodbye Waves along with very thin emaciated ready to melt sea ice near Wrangel Island August 30, the thin ice almost looks like goodbye waves but they are not quite alike. |
August 27-28 , JAXA depiction is fairly good , but there is a mix between Goodbye Waves and sea ice, seen on 28 apparently having more sea ice, although the two are from sea ice, they are definitely not alike, the prominent gap breaking up the ice bridge in two is more prominent on NASA EOSDIS capture (above), the bridge is no more, what is left is going goodbye.
JAXA got the Gap almost the same with EOSDIS on August 29
Goodbye Waves likely caused this confusion. Look at the 2nd arm of the ice bridge reappearing on August 28.
The ice bridge collapsed quicker by the cuts of many cyclones, it was already impossible to walk on
it late July. It now exists like glue holding 2 tons together. WD August 30,2016
Monday, August 29, 2016
Cyclone centring by sea ice footprints? Another North Pole hole miss
North Pole proximity had the visit of an important cyclone approximately 974 mb for about half a day. Again a great deal of open water was created near or at its centre. This prompts the idea of cross checking the real cyclone centre with sea ice imprints, the same goes for very High pressures.
The larger state of current sea ice deteriorates further late in the season as well.August 29, 2016 wd
Sunday, August 28, 2016
Canadian Side usually ultra dense sea ice observed loose up to 89.5N
The latest August 28 974 mb cyclone is very near the Pole, and this time it should create quite a lot of open water there because the Canadian side of Pole sea ice is now likely the least dense observed in history. WDAugust28,2016
Wrangel Island ice bridge methodically becoming no more.
~If it all melts, 2012 extent record will be seriously challenged or exceeded
Within last 4 days, the Wrangel Island ice bridge has lost about half of its extent, at this rate it should be all gone within a week, since the water surface to ice ratio increases every day:
Once the middle of Wrangel Island ice bridge to Pole becomes water, likely in a few days if not tomorrow, the melting will accelerate. Comparing to 2012 is of interest:
There are huge differences between the icescape of August 27, 2016 and same day 2012. 2012 had an ice bridge to Wrangel but disappeared earlier, North of Laptev sea ice was only present above 80 N, the Atlantic front was more to the North. However 2016 has a deeper towards the North Pole sea water bite and has incredible CAB lower density sea ice areas :
The over all up to date review suggests 2016 capable of surpassing 2012 in its own way. Melt years are rarely alike, even one following another. What makes 2016 apart, is that it happened significantly without a prolonged Arctic Dipole, in other words, without a great deal of summer insolation (and its cooler in summer when cloudy, even in the Arctic). This was a prerequisite proving that warming Global Temperatures need not have favourable weather conditions to devastate the existence of Arctic Sea ice. WD August 28,2016
Within last 4 days, the Wrangel Island ice bridge has lost about half of its extent, at this rate it should be all gone within a week, since the water surface to ice ratio increases every day:
Once the middle of Wrangel Island ice bridge to Pole becomes water, likely in a few days if not tomorrow, the melting will accelerate. Comparing to 2012 is of interest:
There are huge differences between the icescape of August 27, 2016 and same day 2012. 2012 had an ice bridge to Wrangel but disappeared earlier, North of Laptev sea ice was only present above 80 N, the Atlantic front was more to the North. However 2016 has a deeper towards the North Pole sea water bite and has incredible CAB lower density sea ice areas :
The over all up to date review suggests 2016 capable of surpassing 2012 in its own way. Melt years are rarely alike, even one following another. What makes 2016 apart, is that it happened significantly without a prolonged Arctic Dipole, in other words, without a great deal of summer insolation (and its cooler in summer when cloudy, even in the Arctic). This was a prerequisite proving that warming Global Temperatures need not have favourable weather conditions to devastate the existence of Arctic Sea ice. WD August 28,2016
Friday, August 26, 2016
Trans Polar Stream, first time so wet in history, is simply huge, it may cause a fluid mix accelerating flushing to the warm North Atlantic.
A gap in clouds drifted long enough to reveal a huge area of sea water mixed with loose sea ice just South of the North Pole (about 100 nautical miles), NOAA HRPT. Of interest is the zone between this opening and Fram Strait, which has always been a fluid area of sea ice, usually slowed by traffic jams of ice coming from multiple directions. However, even in winter, this is an area rife with movement. It may not be strange that it looks more dense with sea ice, it all bunches up there, but it is not a static zone especially now:
Fram Strait is rapidly bulging Southwards with sea ice, this means that the Open Trans Polar Stream may reach the Strait, with 0 to +7 C sea surface temperatures. Notice Goodbye waves between Greenland and Spitsbergen Isles, they expanded from August 23 to 25 as well, a sure indication of rapid melting along with the arrival of new sea ice. If the Trans Polar Stream open zone reaches Fram Strait, it would mean a much more fluid flow of sea ice to the North Atlantic.
Note the zone of open water within the Trans Polar Stream appears far more ominous on Satellite pictures, this is due to AMSR2 15% minimum sea ice per grid rule. However, any increase in fluidity North of Greenland or Spitsbergen would accelerate the flushing of the real last remnant of dense sea ice North of Greenland as the mixing mashed up zone of subduction would have no pressure from the Trans Polar Stream furnishing usually thick ridged sea ice, this acceleration may have already started.. wd August 25, 2016
Fram Strait is rapidly bulging Southwards with sea ice, this means that the Open Trans Polar Stream may reach the Strait, with 0 to +7 C sea surface temperatures. Notice Goodbye waves between Greenland and Spitsbergen Isles, they expanded from August 23 to 25 as well, a sure indication of rapid melting along with the arrival of new sea ice. If the Trans Polar Stream open zone reaches Fram Strait, it would mean a much more fluid flow of sea ice to the North Atlantic.
Note the zone of open water within the Trans Polar Stream appears far more ominous on Satellite pictures, this is due to AMSR2 15% minimum sea ice per grid rule. However, any increase in fluidity North of Greenland or Spitsbergen would accelerate the flushing of the real last remnant of dense sea ice North of Greenland as the mixing mashed up zone of subduction would have no pressure from the Trans Polar Stream furnishing usually thick ridged sea ice, this acceleration may have already started.. wd August 25, 2016
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)